THE CONTINUOUS MOVEMENT of
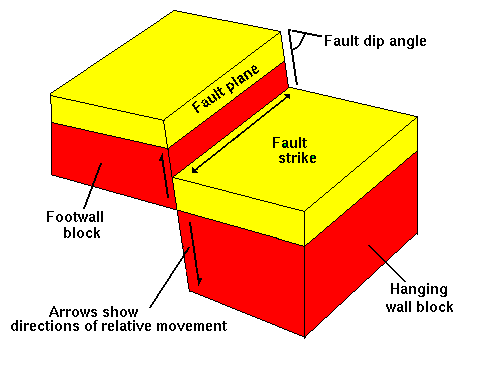
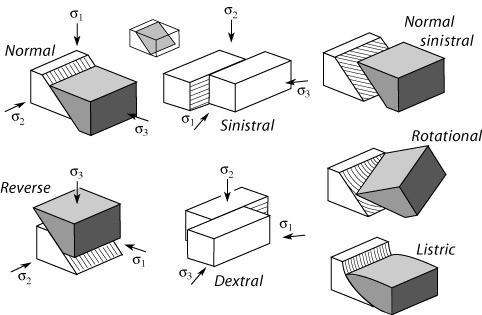
the Earth's crustal plates can squeeze, stretch, or break rock strata, deforming them and producing faults and folds. A faults is a fracture in a rock along which there is movement of one side relative to the other. The movement can be vertical, horizontal or oblique (vertical and horizontal).
 |
| Structure of Fault |
Faults develop when rocks are subjected to compression or tension. They tend to occur in hard, rigid rocks, which are more likely to break than bend. The smallest faults occur in single mineral crystals and are microscopically small, whereas the largest -
the Great Rift Valley in Africa, which formed between 5 million and 100,000 years ago - is more than 9,000 kilometres long.
 |
| The Great Rift Valley |
Examples of Faults:-
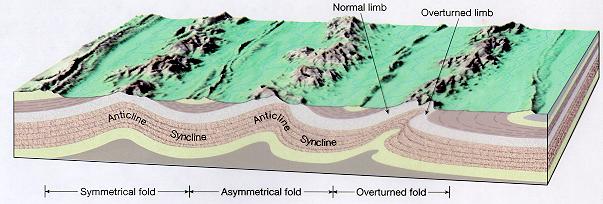
A fold is a bend in a rock layer caused by compression. Folds occur in elastic rocks, which tend to bend rather than break. The two main types of Fold are:-
1.Anticlines (Upfolds)
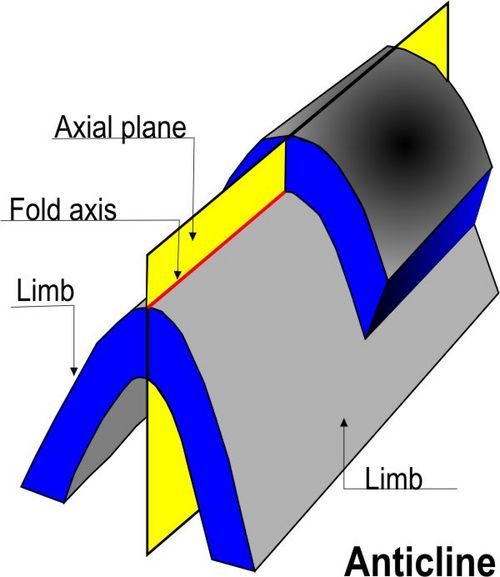 |
| Anticlines (Upfolds) |
2.Synclines (Downfolds)
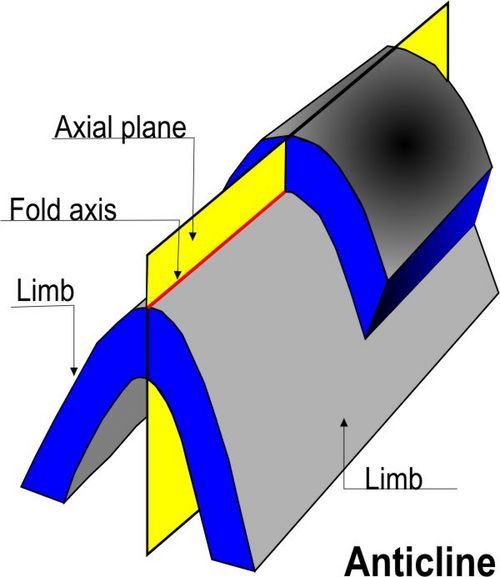 |
| Synclines (Downfolds) |
Folds vary in size from a few millimetres long to folded mountain ranges hundreds of kilometres long, such as the Himalaya and the Alps, which are repeatedly folding.
Examples of Folds:-
In addition to faults and folds, other features associated with Rock Deformation include Boundins, Mullions and en échelon Fractures.




No comments:
Post a Comment
Let me know guys what you think about this.